Venture capital (VC) is a kind of private fund provided by investors to start-ups and small businesses with the potential for progress and growth. The majority of venture money comes from wealthy investors, investment banks, and many financial organizations.

What is risk-taking capital?

In venture capital, money is invested in a business—typically a startup or small business—in return for equity in the enterprise. It is also a significant subset of the private markets, a much more expansive and complicated area of the financial world.
A venture capital company is what?

Startups and other young, frequently tech-focused businesses are funded and mentored by venture capital firms, a sort of investment company. Similar to private equity (PE) firms, venture capital (VC) firms make investments in promising private businesses using funds raised from limited partners. Contrary to PE firms, VC firms frequently acquire a minority stake in the businesses they invest in—50% ownership or less. A company’s portfolio is its collection of businesses, and the actual firms, portfolio companies. Venture capital companies include, for instance:
Capital Sequoia

Sequoia Capital is a venture capital company with its headquarters in Menlo Park, California. It invests in a variety of industries, including media, retail, energy, mobile, and the internet. The company has invested in businesses like Uber, Bird, DoorDash, and 23andMe and is a prominent investor in ghost kitchens, an emerging market tracked by PitchBook.
With Andreessen Capital

A venture capital company with its headquarters in Menlo Park, Andreessen Horowitz has backed businesses like Lime, Airbnb, Instacart, and Foursquare. The company established a $2.2 billion cryptocurrency fund in June 2021, the biggest of its kind and a step up in venture capitalists’ efforts to support blockchain-focused startups.
The London-based early-stage venture capital firm DN Capital finances firms in software, fintech, mobile app, digital media, e-commerce, and other sectors. DN Capital, a company established in 2000, helped launch well-known startups like Shazam, Auto1, and Purplebricks. A venture capital fund is what?
Venture capital firms establish a fund and solicit pledges from limited partners to raise the funds necessary to invest in businesses. They can create a fund through this process, which they then use to invest in potential private businesses. Their investments are usually made in exchange for minority equity, which is a stake in the business of 50% or less.
A top Dutch venture capital firm is BioGeneration Ventures II, for instance. It invests in healthcare businesses at seed, early, and late phases and is based in Naarden, the Netherlands. Edward van Wezel is the company’s founder and manager. The completely invested fund has provided funding to a number of businesses, including the drug discovery startups Cristal Therapeutics and Synaffix.
A venture investor is what?

The term “venture capitalist” refers to investors who work for a venture capital company. They help raise money for venture funds and actively look for investment possibilities for the business. According to statistics from PitchBook, there were 9,960 active VC investors worldwide in 2021. To put that into context, there are currently 599% more active VCs than there were in 2007. Using the prior section as an example, venture capitalist Edward van Wezel works for BioGeneration Ventures.
What distinguishes venture financiers from angel investors?

While a venture capitalist raises and invests capital from limited partners, an angel investor is a wealthy person who invests their own money into promising businesses. On ABC’s Shark Tank, regular backers Mark Cuban and Lori Greiner, as illustrations of angel donors.
What is the process of venture capital?
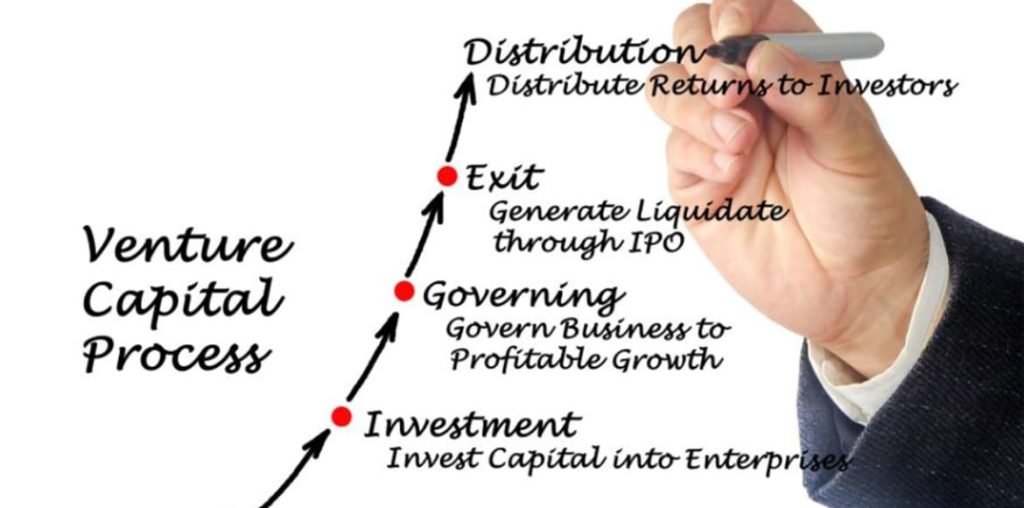
Businesses go through various phases of venture capital as they develop. Additionally, businesses or investors might concentrate particularly on a certain stage, which has an effect on how they spend. A seed round is when a venture capitalist invests a relatively small amount of money in a startup to be used for business plan development, market research, or product development. A seed round, as its name implies, is frequently the company’s first formal round of institutional financing. In return for their investments, seed round investors frequently receive convertible notes, equity, or preferred stock options. Nosso, a fintech startup based in Cambridge, England, received $2.7 million in seed money in February 2022.
Early-stage

Companies in the development stage are the target audience for venture capital financing in the early stages. Due to the fact that new companies require more capital to launch operations once they have a viable product or service, this stage of financing typically has a higher funding amount than the seed stage. The rounds or series in which venture capital is deposited are identified by letters: Series A, Series B, Series C, and so on. San Francisco-based Planet FWD, which was established in 2019, received $9.96 million in early-stage Series A venture capital financing in May 2022.
Late-stage

The late stage of venture capital financing is for more established businesses with demonstrated revenue generation and growth, whether or not they are yet profitable. Each round or series has a name assigned to it similar to the early stage. Although late-stage financing rounds can go up to a Series K, Series D, Series E, and Series F are more typical. As an illustration, Seattle-based Glowforge, a producer of 3D laser printers, received $43 million in Series E funding at a late stage in June 2022.
A venture capital firm makes money and distributes returns to the limited partners who invested in its fund if a company it has invested in is purchased or goes public. Selling some of its stock to another investor in what is known as the secondary market would also be profitable for the company.















