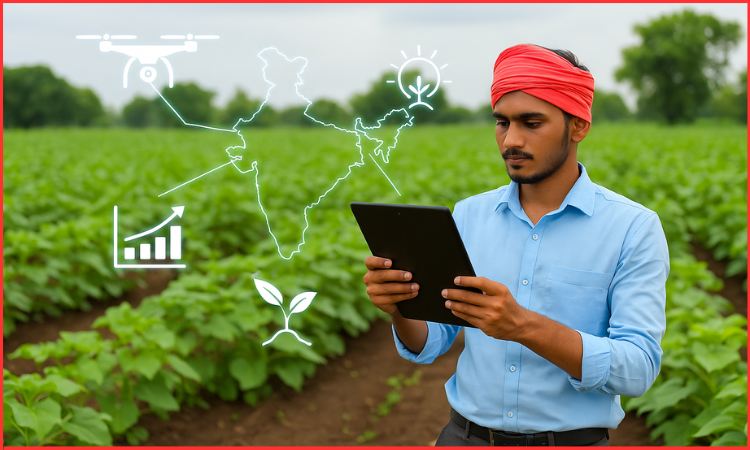
Agriculture has always been the heart of the Indian economy, even after India’s shift toward a service-based economy. Today, farming continues to sustain nearly half of India’s rural population. This makes agriculture vital for food security, rural employment, and sustainable growth. Agritech startups in India are now playing a crucial role in transforming traditional farming practices.
By leveraging tools like AI, IoT, drones, blockchain, and data analytics, these startups are shaping the future of farming. Technology adoption not only boosts productivity but also tackles challenges like climate risks, post-harvest losses, and limited market access. In this article, we explore India’s key agritech innovations, their impact on farmers, adoption challenges, and the sector’s future.
Key factors driving the rapid growth of Agritech in India

After the pandemic, the agritech sector in India has grown at an increasingly high speed. This makes India one of the fastest-growing agritech markets. The following are some of the factors that have fuelled the agritech industry’s explosive growth:
Growing Digital Platform Usage in Rural India
Farmers are now able to easily access mobile platforms and connect with online marketplaces. This has been made possible by the availability of affordable smartphones and better internet access in rural India.
Disruptions in the Supply Chain
The pandemic has brought highlight on several inefficiencies in India’s conventional agri-supply chains. As a result, the need for tech-enabled logistics, direct farmer-to-consumer platforms, and storage solutions has increased.
Increasing Demand for Quality Produce
Consumers today want to know from their food is coming from. They are demanding premium agricultural products. Thus, the demand for agritech to ensure standardisation, grading, and quality checks is rising.
Rise in Private Equity and Venture Capital
Investors recognise the immense potential of Agritech startups in India, leading to significant funding that helps farmers scale production and access better tools.
Key Innovations & Technologies developed by Agritech Startups:
Source: FruPro
Precision farming with AI and IoT
Precision farming allows for more accurate use of resources like water, fertilisers, and pesticides. This leads to improved efficiency and a smaller environmental impact. It relies on sensors, connected devices, and AI models to help farmers make better decisions. IoT sensors monitor soil health, moisture, and nutrient levels in real-time. AI analyses this data to guide irrigation, fertiliser use, and crop cycles for farmers.
Drones and Remote Sensing
Drones equipped with multispectral and thermal cameras help to detect pest infestations early and water-stressed areas by scanning the fields. This lets farmers address issues before they affect the entire crop field. With remote sensing by satellites, the tracking of large-scale climate, rainfall, and vegetation patterns has become easier. Thus, drones and remote sensing have helped in replacing the inconsistent guesswork of farmers.
Blockchain for Transparency
Problems with the quality of produce, authenticity, and price are common among farmers and consumers. Thus, by using blockchain, a digital ledger that is tamper-proof is developed. By using this digital ledger, consumers can verify the product’s authenticity, and farmers can gain more credibility and increase their profits by removing the role of middlemen.
Hydroponics and Vertical Farming Practices
The demand for farming methods that use less space and soil is increasing in urban areas. Hydroponics can be used in urban farming, which relies on nutrient-rich water instead of soil. Also, vertical farming can thrive in limited environments. These methods significantly lower water usage and allow for year-round cultivation in cities.
Online Marketplaces
Online marketplaces help to connect farmers directly with buyers and reduce the role of middlemen. These platforms offer farmers and buyers many benefits, like fair pricing, bulk demand access, and logistics support. Thus, with the increase in the use of smartphones in rural India, online platforms have gained significance among small and marginal farmers.
Data-driven Farming Solutions
Big data analytics helps to ease the use of large amounts of data on climate, soil maps, and years of crop yields to predict future outcomes. By using these insights, farmers are selecting the right crops for their land, planning irrigation schedules, or ensuring their crops grow more accurately. Governments are also using this data to develop better agricultural policies and prepare for disasters.
Supply Chain Technology
In agricultural supply chains, majorly issues result in post-harvest losses. However, cold chain management, smart logistics, and digital inventory tracking are overcoming this problem. Real-time data ensures produce reaches markets faster and fresher, reducing wastage and improving farmer income. Especially for exporters, these tech-enabled supply chains help them to fulfil the required international quality standards.
Machine-based Quality Management
Previously, sorting and grading the agricultural outcome manually was time-consuming and inconsistent. But today, with AI-enabled machines and computer vision, fruits, vegetables, and grains can be easily graded based on size, colour, and ripeness. This helps farmers to maintain consistent quality, maintain trust with buyers, and offer better prices in exports.
Impact of Agritech on Farmers
Increased Productivity with Fewer Inputs
With the help of technology and practices like precision farming, IoT sensors, and AI-powered platforms, farmers are now using the right amount of water, fertiliser, and pesticide. Thus, reducing the input cost while boosting productivity and leading to more output per acre and higher income.
Reduced Risk and Uncertainty
India’s agriculture has always been affected by unpredictable weather. But with agritech startups, the uncertainty has been reduced. Weather apps, satellite data, and predictive analytics help farmers to prepare for droughts, floods, or heatwaves. Thus, data-driven crop planning has reduced risk and uncertainty.
Better Market Access
Before, middlemen used to take a large benefit from farmer profits. However, online marketplaces and blockchain-based supply chains create more transparency and help farmers connect directly with buyers, supermarkets, and exporters. Thus, farmers get a chance to offer better prices and payment security.
Lower Post-harvest Losses
Majorly, farmers face a loss in the leftover agricultural output due to poor storage and transport delays. However, with supply chain tech, cold storage, smart logistics, and real-time tracking, the loss has been reduced. Additionally, with online platforms, the farmers’ produce reaches buyers in no time, reducing the probability of post-harvest loss.
Access to credit and insurance
Data-driven platforms also solve the problem of a lack of formal credit. Banks and NBFCs don’t lend frequently to farmers because of uncertain farm records. However, these agritech platforms analyse farm data like yield history and soil health to lend credit to farmers. Hence, making credit more accessible for farmers.
Challenges responsible for the Slow adoption of Agritech
Digital literacy
Though the adoption of online tools and platforms in rural areas is increasing, farmers still lack the skills to use apps and online tools efficiently. Thus, the lack of local-language interfaces or voice-based solutions makes adoption harder.
Inefficient Supply of Power
Intermittent electricity or weak mobile signals make real-time apps unreliable. Due to a weak power supply, the use of IoT devices, cold storage, and even charging smartphones gets significantly impacted.
High Upfront Costs
These innovative devices, like IoT sensors, AI-enabled machinery, and hydroponic setups, require high investments. Hence, Agritech becomes a luxury for a large number of farmers, excluding the problems of small and marginal farmers.
Data Privacy
The agritech sector majorly relies on heavy data, including farmer financial details. Due to a lack of strong data-protection frameworks in rural India, farmers fear exploitation if their data is shared with traders or insurance companies.
Trust barriers
Farming in India is deeply traditional. Local agri-tech dealers and middlemen often discourage farmers from adopting new technology to maintain their roles and profits. Therefore, many startups in the past have failed to gain acceptance in rural communities.
Future of Agritech in India

By 2030, India is projected to become one of the world’s largest agritech markets, driven by AI-powered advisory tools, precision farming, drones, and digital marketplaces. However, scalability depends on making technology affordable, inclusive, and farmer-friendly. As rural internet penetration strengthens, small and marginal farmers are expected to adopt technology to boost yields and reduce risks.
If challenges like affordability, infrastructure, and trust are addressed, Agritech startups in India could make Indian farming more resilient, climate-smart, and globally competitive.
Final Thoughts
Agritech in India is no longer just about gadgets or digital apps. It focuses on making farming a more profitable, predictable, and sustainable way of life for millions of farmers. Startups are developing solutions to India’s key agricultural issues, ranging from AI-driven precision farming to blockchain-based supply chains.
The future will require better farmer education, affordable technology, and improved rural infrastructure. In 2025 and beyond, Agritech startups in India will continue to boost productivity, strengthen food security, and support sustainability while positioning India as a global agricultural leader.
FAQs
Q1. What is the current market size of agritech in India?
According to a study by EY, India’s agritech market is expected to reach $24 billion by FY 2025-26.
Q2. What challenges are slowing agritech adoption in India?
Key challenges include low digital literacy, inconsistent electricity and internet, high upfront costs, data privacy concerns, and resistance to change.
Q3. What are the key innovations of agritech startups in India?
Innovations include AI- and IoT-powered precision farming, satellite-based crop monitoring, blockchain for transparency, hydroponics, and vertical farming.















